The functions for 3D reconstruction as well as all the Image Filters are included in all of the X-Series programs.
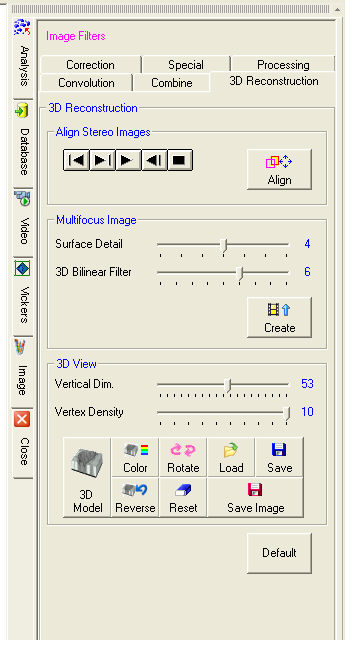
To be able to obtain the three-dimensional (3D) model of a surface it
is necessary to have a sequence of partially in-focus images acquired
with different focal planes (obtained by progressive steps).
The best reconstruction is obtained by acquiring the first image starting
from the lowest plane.
The following images are obtained by rotating the microscope's focusing
mechanism upwards trying to maintain a constant step between one image
and the next.
![]() Some microscopes have a motorized Z-axis and thus this operation
may be automatic.
Some microscopes have a motorized Z-axis and thus this operation
may be automatic.
If images are acquired by a stero microscope lacking the tool for the correction of the angle of view, it is necessary to perform an alignment of the images.
Images acquired with a stereo microscope are slightly off-centered.
Acquire the image sequence starting from the lowest plane. The step between
one image and the next must be selected so that the focus of the whole
field of view is covered by the image sequence.
Once the sequence is acquired and the images are loaded, press ![]() .
.
The animation of the aligned acquired images is dispayed.
The ![]() commands control the animation. Back one image, Forward
one image, Play, Back to first image, and Stop. The alignment is automatic
but you can correct manually the position of each single image.
commands control the animation. Back one image, Forward
one image, Play, Back to first image, and Stop. The alignment is automatic
but you can correct manually the position of each single image.
If the animation shows an imperfect alignment, go to the image to be corrected
and use the arrow keys on the keyboard. The corresponding position of
the image in the sequence is displayed in X and Y coordinates on the Title
Bar.
The performed correction can be verified by displaying alternatively the
previous image and the following one with the ![]() commands.
commands.
The construction of the multifocus image employs a maximum variance
algorithm. The Surface Detail
cursor acts on the kernel of the maximum variance filter. By increasing
this value, the resulting multifocus image definition increases too, but
so does the processing time.
The 3D Bilinear Filter acts on
the three-dimensional model that will be created, correcting any zones
which have failed to be in-focus in any of the images in the sequence.
The higher its value, the higher the degree of softening of the 3D surface.
The ![]() button starts the construction of the multifocus image
and the 3D model.
button starts the construction of the multifocus image
and the 3D model.
At the end the resulting multifocus image is displayed.
![]() The last 3D model created is saved automatically and can
be recalled at any moment with the 3D display button.
The last 3D model created is saved automatically and can
be recalled at any moment with the 3D display button.
The Vertical Dim. cursor controls
the vertical dimension of the 3D model, while the Vertex
Density controls the number of 3D points used for the construction
of the 3D surface. ![]() To display the
effect it is necessary to press the 3D display button.
To display the
effect it is necessary to press the 3D display button.
The 3D display button  allows you to display the 3D
model,
allows you to display the 3D
model, ![]() displays the reverse and
displays the reverse and ![]() displays
it in the color scale.
displays
it in the color scale.
![]() On the model's lower surface is diplayed the reconstructed
multifocus image, which can be useful for a 2D/3D visual comparison.
On the model's lower surface is diplayed the reconstructed
multifocus image, which can be useful for a 2D/3D visual comparison.
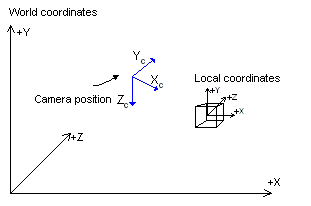
On the 3D window the left mouse button allows you to rotate the model wheras the right mouse button controls the translation.
The + (plus) and - (minus) characters on the numeric keypad control the zoom.
The Q and E characters on the keyboard control the camera's horizontal rotation whereas the A and Z keys control the vertical rotation.
The ![]() button performs a model rotation with respect to
the vertical axis.
button performs a model rotation with respect to
the vertical axis.
The ![]() button displays the model in its initial state.
button displays the model in its initial state.
The ![]() buttons control the storing in standard DirectX.
buttons control the storing in standard DirectX.
The ![]() button allows you to save the 3D image as a static
image which can be useful, for example, to generate a professional report.
button allows you to save the 3D image as a static
image which can be useful, for example, to generate a professional report.
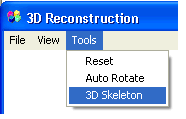 The 3D Reconstruction window menu, as well as containing
the commands mentioned above, also contains the 3D
Skeleton command which activates the vectorial display of the surface.
The 3D Reconstruction window menu, as well as containing
the commands mentioned above, also contains the 3D
Skeleton command which activates the vectorial display of the surface.